Efficient LLM Training & Inference
Research on making large language models more efficient to train and deploy
This project focuses on developing novel methods to make training and deploying large language models more efficient and accessible, with techniques spanning compression, optimization, and low-rank adaptation.
Memory-Efficient Training
Flora: Low-Rank Adapters as Gradient Compressors
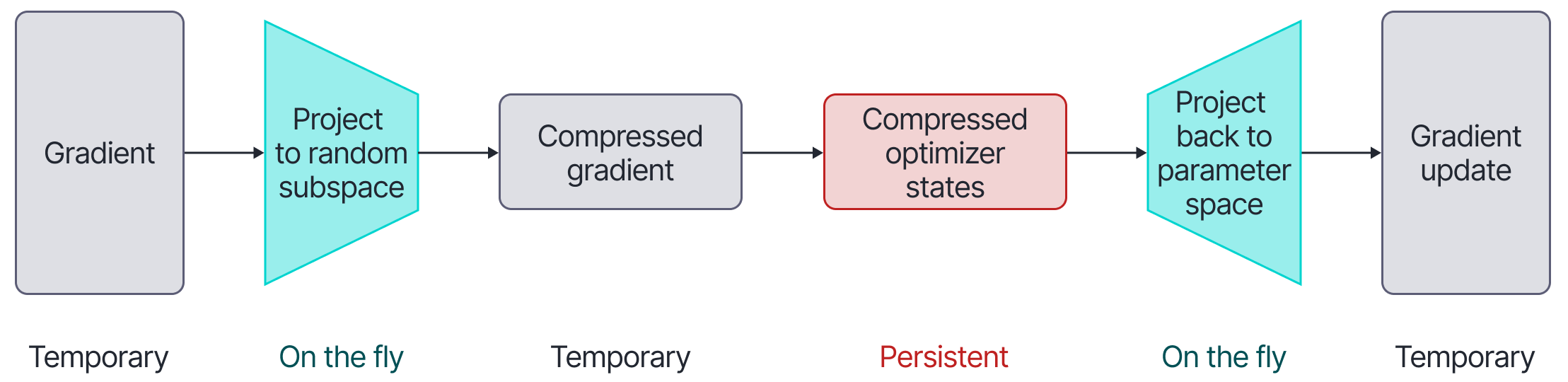
We discovered that low-rank adapters (LoRA) can be viewed as random projection-based gradient compression. Based on this insight, we developed Flora, which achieves high-rank updates while maintaining the memory efficiency of LoRA. This enables training multi-billion parameter LLMs on a single GPU.
NeuZip: Dynamic Neural Network Compression
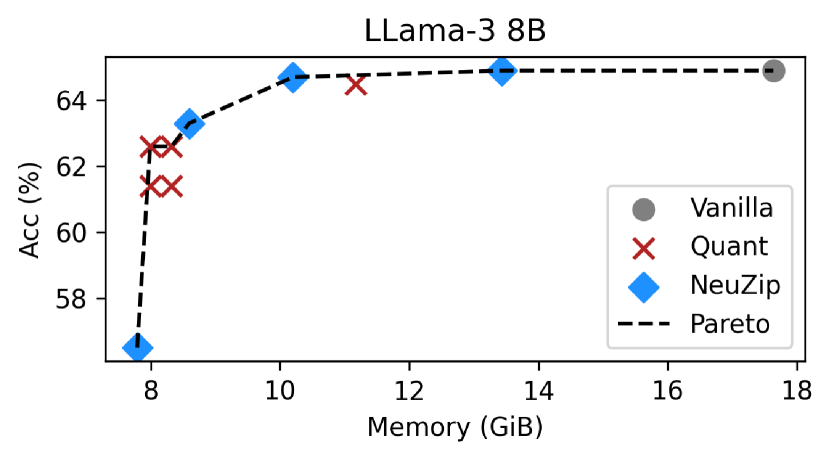
We introduced NeuZip, a novel weight compression scheme based on the entropy of floating-point numbers in neural networks. This enables memory-efficient training and inference without performance degradation, reducing the memory footprint of Llama-3 8B from 31GB to under 16GB.
InvarExplore: Ultra-Low-Bit Model Quantization
We developed InvarExplore, a unified framework for ultra-low-bit quantization (e.g., 2 bits) that systematically explores different types of model invariance simultaneously. The framework features a novel discrete search algorithm that enables exploration of permutation invariance - an aspect that traditional gradient-based methods cannot optimize. InvarExplore achieves additional performance improvements when combined with existing state-of-the-art quantization methods.
Ginger: Efficient Curvature Approximation
A novel approach to approximate curvature information in neural networks with linear complexity, enabling more efficient optimization for large models while maintaining convergence guarantees.
Impact
This research has advanced the field of efficient deep learning by:
- Enabling training of multi-billion parameter models on limited hardware
- Developing novel compression techniques for both training and inference
- Creating efficient optimization methods with theoretical guarantees
- Making LLM training and deployment more accessible
- Providing insights into the relationship between model compression and optimization
The methods have been successfully applied to train and deploy large language models with significantly reduced computational requirements, making advanced AI more accessible to researchers and practitioners with limited computing resources.